Discussing the New Tokenomics Proposal: Monthly Block Producer Meeting—April 2024
The EOS Block Producer (BP) monthly meetings serve as a foundational platform for facilitating consistent and open communication between the top 30 EOS BPs and the EOS Network Foundation (ENF). These gatherings are designed to cultivate a collaborative environment where network operators and custodians can engage in constructive dialogue, share insights, and work collectively towards the shared goal of advancing and strengthening the EOS ecosystem. Through these discussions, the community aims to address challenges, explore new opportunities, and implement strategies that align with the network’s long-term vision for innovation and growth.
Meeting Overview
The meeting commenced at 0100 UTC on April 25th, 2024, with 20 Block Producers (BPs) and a total of 30 attendees participating. To accommodate the diverse, global audience, the Interprefy tool was employed for real-time translation across multiple languages, facilitating effective communication throughout the session.
Beatrice Wang, Communications Manager for the EOS Network Foundation (ENF), welcomed participants and introduced the agenda.
The call was led by Yves La Rose, CEO and Founder of the EOS Network Foundation (ENF), who focused on presenting the new EOS tokenomics proposal and integrating community feedback into the strategic planning process. Yves steered the discussion towards critical issues such as the implementation of a new tokenomics structure and ensuring stakeholder transparency. This session provided a vital platform for a diverse group of stakeholders to actively participate in refining the network’s economic model and discussing strategic directions.
Prior to the BP call Yves shared this update on X:
Opening Remarks
- Summary of Ongoing Efforts: Yves provided an overview of the efforts undertaken since the last discussion. He emphasized the active involvement of various stakeholders, including block producers, token holders, and developers, in refining the tokenomics proposals based on feedback received.
- Engagement with Stakeholders: Stressing the collaborative approach of the ENF, Yves noted that the feedback and suggestions from the community had been integral to shaping the revised tokenomics proposal. He expressed appreciation for the community’s proactive engagement and their contributions to making the EOS ecosystem more robust and aligned with broader market and technological trends.
- Objective of the Call: Yves clearly outlined that the primary goal of this call was to further discuss these updates, ensure that the community’s views are adequately represented in the decision-making process, and prepare the groundwork for implementing these changes, pending community approval and consensus.
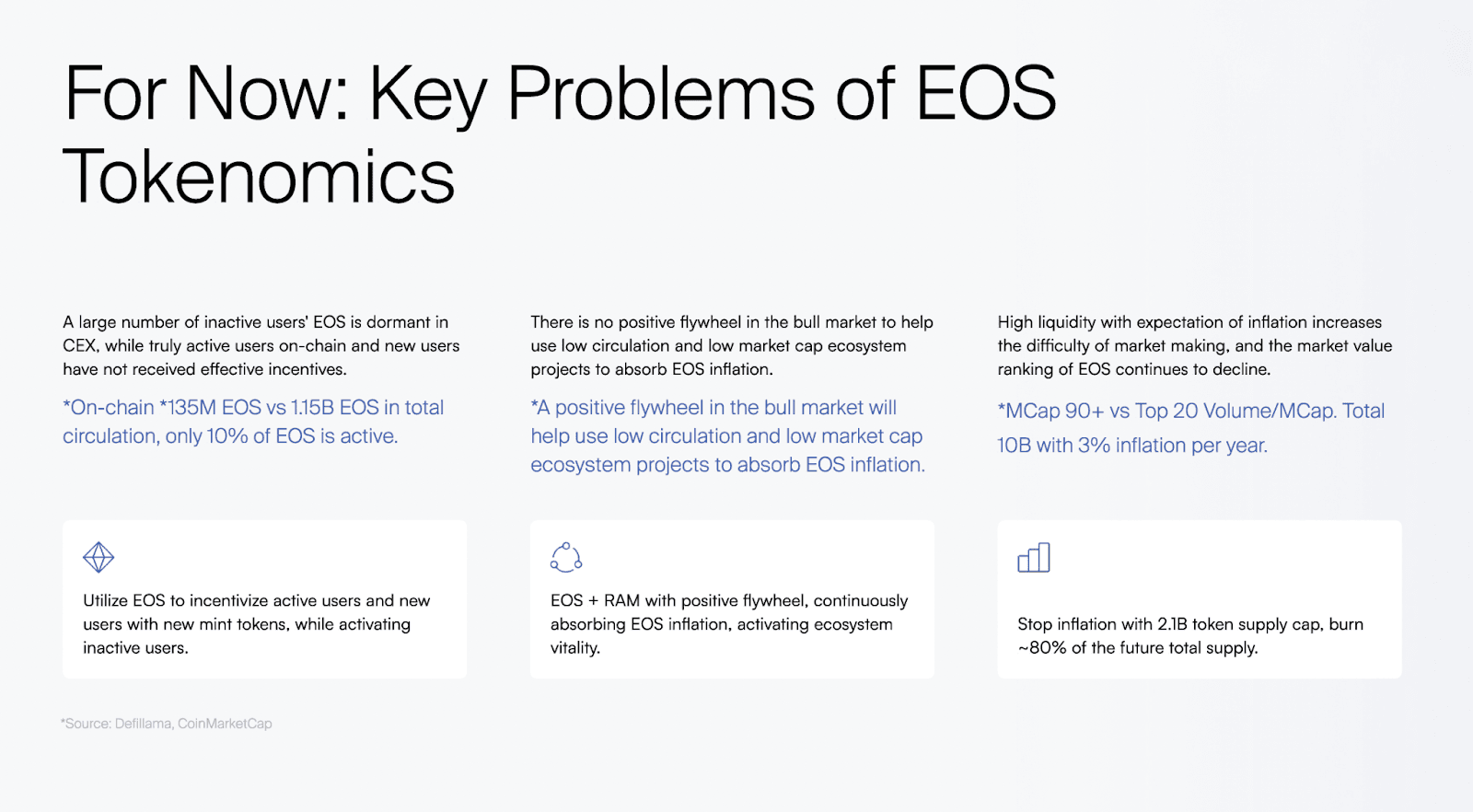
EOS Tokenomics Proposal
During the meeting, Yves La Rose provided a comprehensive overview of the current and future state of EOS tokenomics. He clarified that EOS currently has a maximum token supply of 10 billion tokens, which is hardcoded into the system. This cap, fundamental to the EOS blockchain’s design and governance, counters the misconceptions perpetuated by some cryptocurrency tracking platforms that inaccurately display an infinite supply.
Yves introduced a critical shift in the EOS token supply by proposing a significant reduction of the future token supply by roughly 80%. The new proposal aims to cap the EOS token supply at 2.1 billion tokens, transitioning from an inflationary to a fixed token supply. This change aligns EOS with successful cryptocurrency models like Bitcoin, which has a well-known fixed supply cap of 21 million tokens.
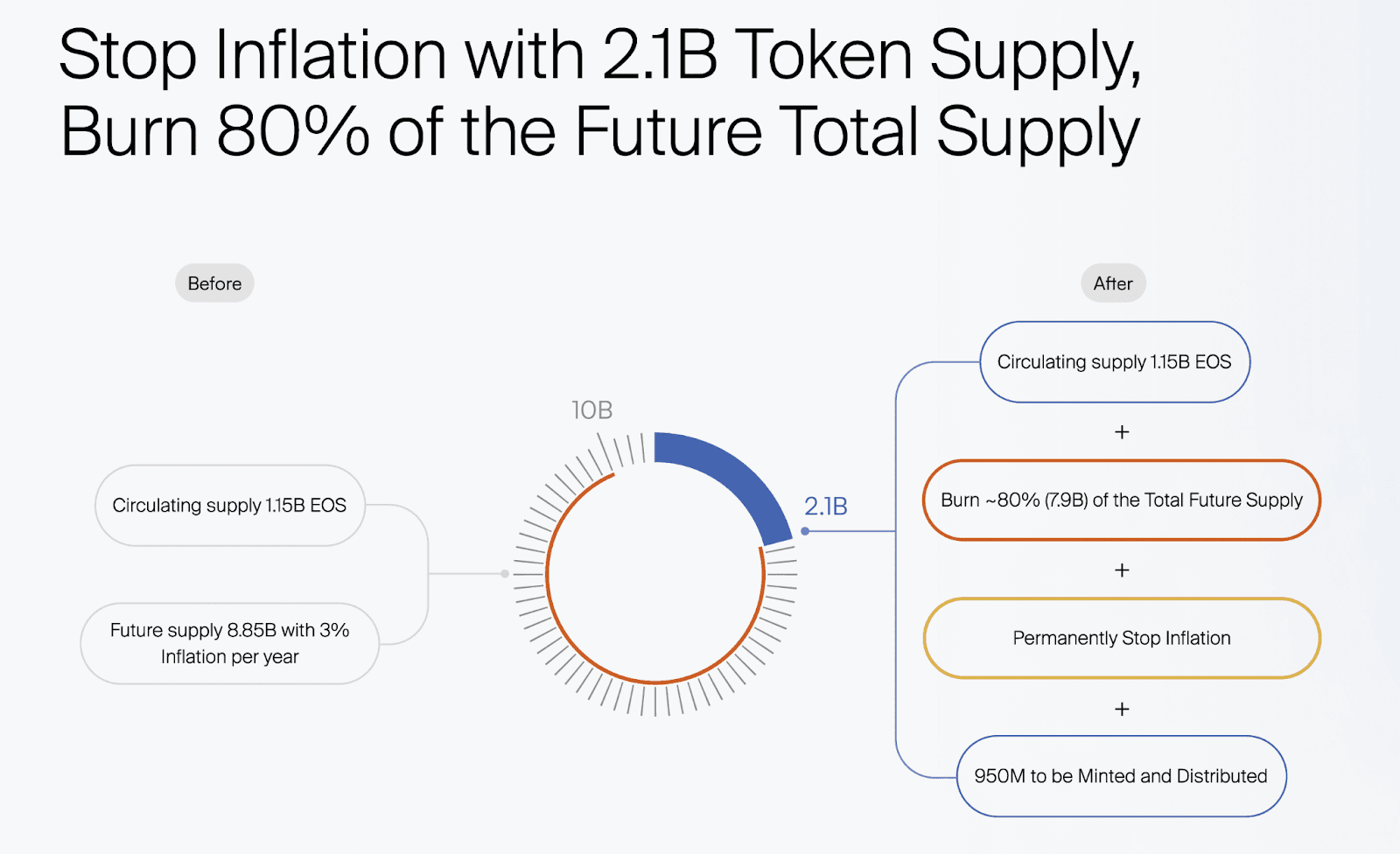
Proposal Details:
- Fixed Token Supply: Transitioning to a fixed token supply of 2.1B tokens, moving away from the inflationary model.
- Alignment with Bitcoin Narrative: The choice of 2.1 billion tokens is strategically chosen to parallel Bitcoin’s cap of 21 million, enhancing the appeal and stability of EOS.
- Market Preference for Fixed Supply: The market has shown a preference for fixed supplies as they provide predictability and help establish a token’s scarcity.
- Token Distribution Strategy: The fixed supply will be allocated across multiple “buckets” for various purposes including network development, ecosystem growth, investment, grants, and staking rewards, similar to most ERC-20 and protocol tokens.
- Market Stability and Appeal: The reduction in supply is expected to enhance both the stability of the EOS token in the market and its appeal to investors. This strategy is anticipated to lead to increased demand and increase ecosystem value, benefiting all stakeholders.
These proposed changes are designed not only to enhance the stability of the EOS token in the market but also to improve its appeal to both current and potential investors, marking a significant shift towards ensuring the EOS ecosystem remains competitive and relevant in the evolving blockchain space.
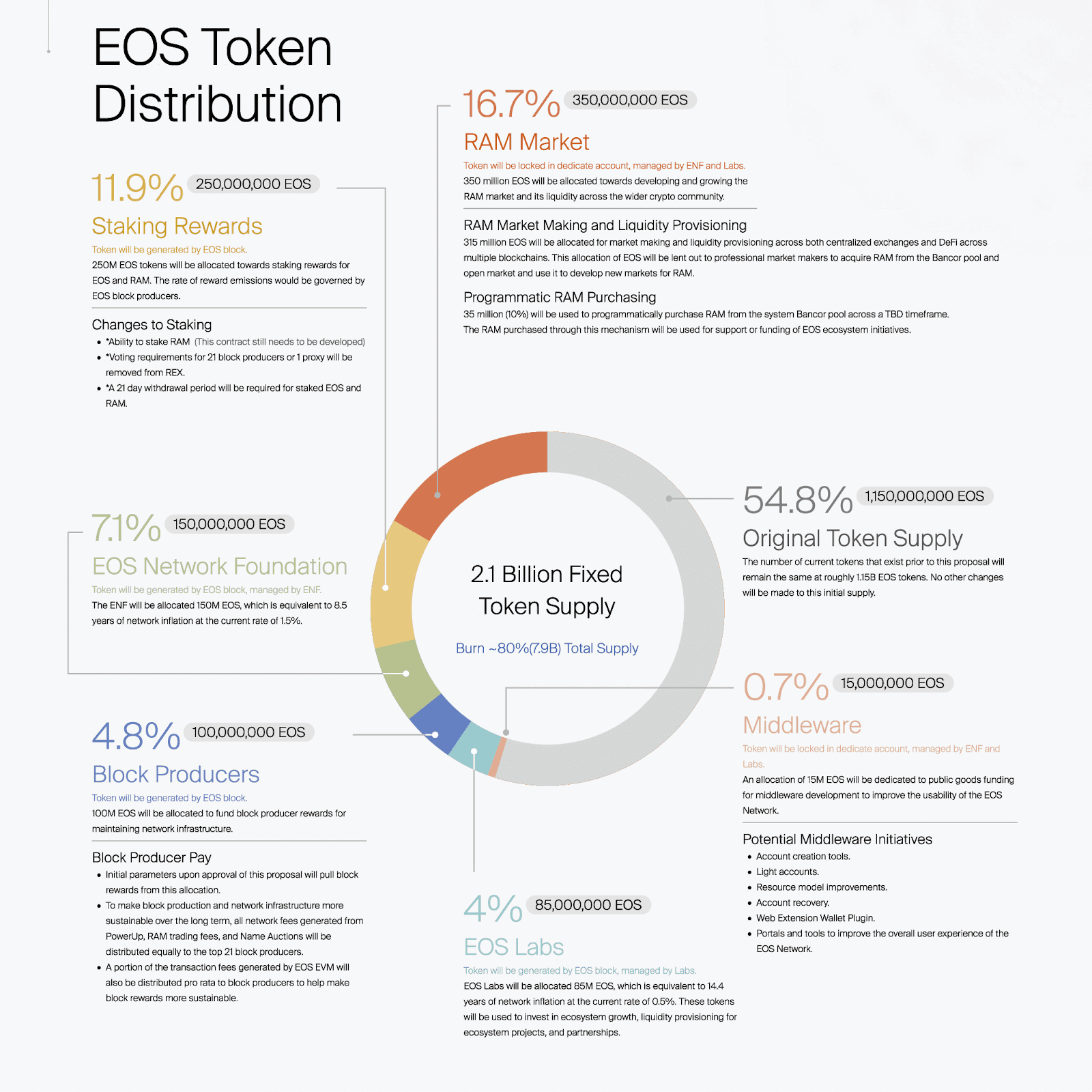
Discussion on Token Allocation and Vesting
Yves La Rose introduced a comprehensive update to the EOS tokenomics during the meeting, emphasizing a strategic shift from an inflationary to a fixed token supply model.
Middleware Bucket Allocation
An immediate allocation of 15 million EOS tokens would be designated for middleware operations, which are critical for enhancing the functionality and user experience of the EOS Network.
Yves was explicit about the planned allocation for these funds, stating, “The intent for this bucket is to allocate, if not all of it, the majority of it, to Greymass.” He praised Greymass for their exceptional capabilities in handling middleware, describing them as an amazing team that has consistently delivered high-quality work. Yves remarked, “And the idea would be that because these tokens are liquid, it also gives Greymass the confidence that there is money available for them to be able to scale rapidly.”
He elaborated on the nature of the funding, emphasizing that it was not an investment but a grant aimed at fostering public goods: “This to close gaps that exist with specific parts of the software that we’ve not been able to address, especially as it comes to UX, UI.” The funding strategy is designed to allow Greymass to work closely with ENF and Labs, leveraging the lessons learned from past collaborations to ensure that the resources are used effectively and promptly.
This approach underscores the commitment to supporting crucial infrastructure developments without requiring equity or ownership stakes in return, ensuring that the benefits of this work are accessible to the entire EOS community.
RAM Market Allocation
A total of 350 million EOS tokens would be allocated to enhance and develop the RAM market, critical for the EOS ecosystem’s operational efficiency and scalability. This substantial allocation is managed by the EOS Network Foundation (ENF) and Labs, with approval from Block Producers, ensuring that the funds are used strategically and transparently.
- RAM Purchasing: Out of the total allocation, 35 million EOS will be used to purchase RAM from the system’s Bancor pool over a timeframe yet to be determined. This targeted purchasing is intended to support or fund various EOS ecosystem initiatives by ensuring adequate RAM availability for ongoing and future projects.
- RAM Market Making and Liquidity Provisioning: The majority of the RAM allocation, amounting to 315 million EOS, is designated for market making and liquidity provisioning. This portion of the funds will be lent out to professional market makers who will acquire RAM from the Bancor pool and the open market. The objective is to use these resources to develop new markets for RAM across centralized exchanges, decentralized exchanges (DEXes), and DeFi protocols on EOS and other blockchain platforms.
This strategic use of the RAM bucket is designed to foster greater liquidity and market stability for RAM within the EOS ecosystem, supporting broader network initiatives and ensuring that EOS remains competitive and functional across diverse crypto environments.
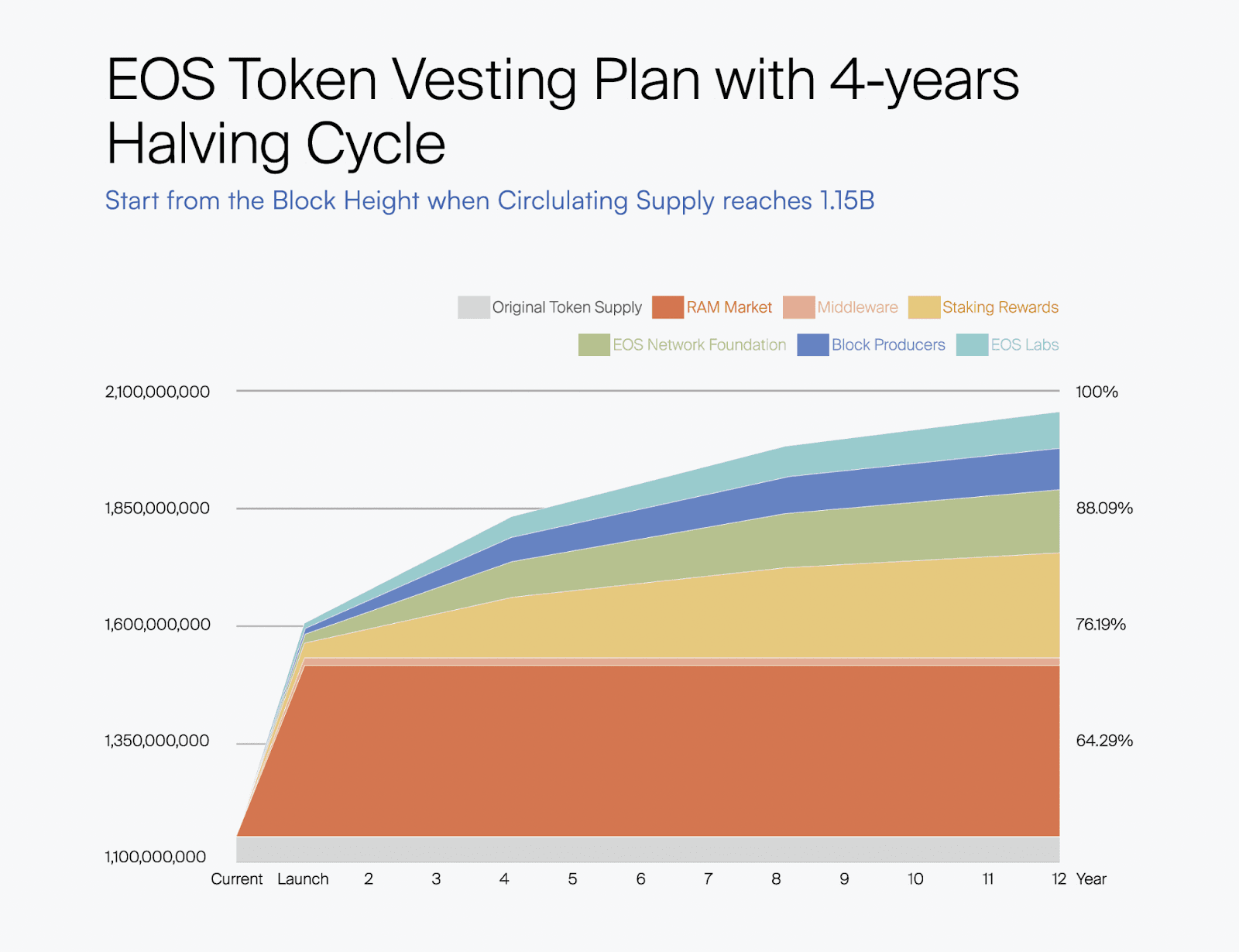
Vesting Schedule for Long-Term Stability
The vesting schedule for EOS’s token allocation is designed to ensure long-term stability and strategic growth across different areas of the EOS ecosystem. Each bucket addresses specific needs and roles within the network, from staking incentives to infrastructure support and development initiatives.
See the EOS Tokenomics Data spreadsheet for a more in depth look at the proposed schedules.
Staking Rewards Bucket
The Staking Rewards Bucket will consist of roughly 250 million EOS tokens allocated to incentivize network participation and security. This bucket is crucial for maintaining the robustness of the EOS blockchain, as these tokens are intended to reward users for staking their EOS tokens, thereby securing the network. The release of these tokens is governed by EOS block producers and is scheduled to occur gradually to ensure a sustained incentive that aligns with the network’s growth and security needs over time.
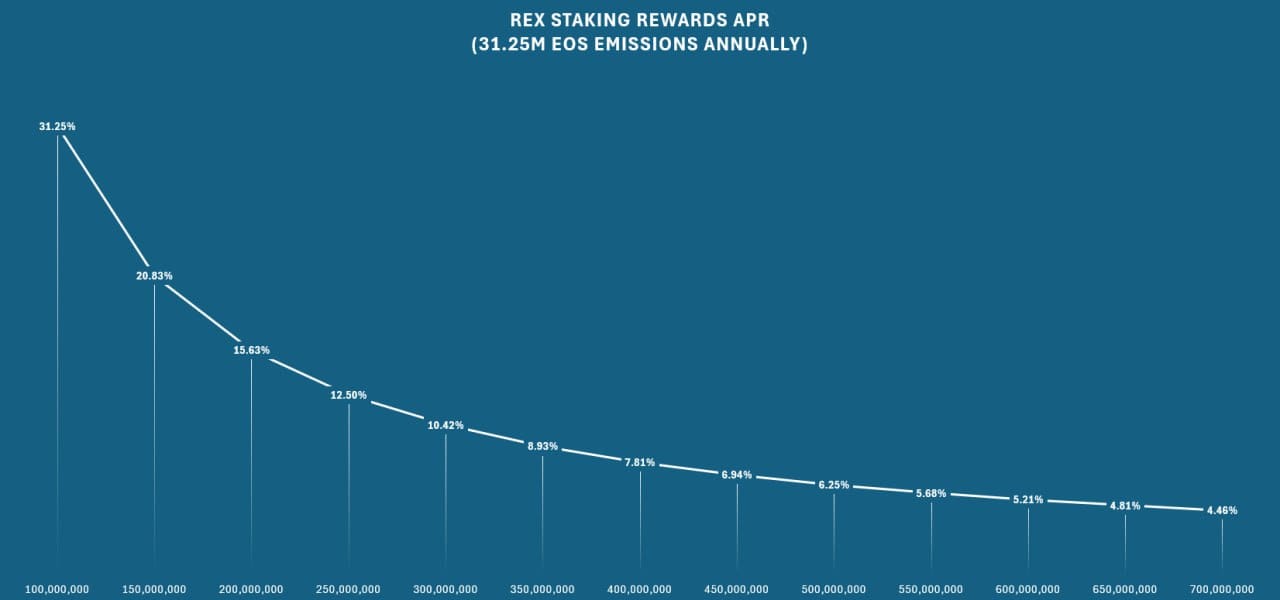
This chart assumes full utilization of the vested tokens from the Staking Rewards Bucket during the first four years. Following the initial halving schedule, the quantities will be reduced by 50%.
Block Producers Bucket
The Block Producers Bucket allocates 100 million EOS tokens to fund the rewards for block producers, who are essential for maintaining the network infrastructure. This funding includes a structured reward system that draws from this allocation over a four-year halving cycle, mimicking Bitcoin’s model. Additionally, this bucket also ensures the distribution of network fees generated from PowerUp, RAM trading, Name Auctions, and EOS EVM transaction fees to top block producers. This structured approach aims to reinforce the infrastructure’s stability, sustainably support, and further align incentives with block producers and the EOS Network, encouraging ongoing investment and participation.
EOS Network Foundation (ENF) Bucket
The ENF Bucket is allocated 150 million EOS tokens to support the operations and development of projects managed by the ENF. This funding is designed to cover approximately 8.5 years of network operations, based on the current rate of network inflation. The ENF uses these funds to drive various initiatives that aim to enhance the EOS platform’s capabilities and outreach, ensuring the ecosystem remains innovative and competitive.
The token release schedule for the ENF Bucket follows a structure that mirrors the initial rate of distribution—releasing about 18,750,000 tokens annually for the first four years. After the first halving cycle, the annual release will be halved to 9,375,000 tokens, aligning with the network’s broader economic strategy to ensure long-term sustainability and reduced inflationary pressure.
EOS Labs Bucket
The EOS Labs Bucket allocates 85 million EOS tokens to fund the activities of EOS Labs, which focuses on ecosystem growth, liquidity provisioning, and forging strategic partnerships. This allocation is equivalent to about 14.4 years of network inflation at the current rate, offering substantial support for EOS Labs to pursue long-term projects that contribute to the ecosystem’s health and expansion. EOS Labs plays a pivotal role in experimenting with and implementing new technologies and solutions within the EOS network, thus driving its overall progress and adaptability.
Similar to the ENF Bucket, the EOS Labs token release will also be subject to a halving every four years, ensuring that the distribution is gradually reduced to manage inflation effectively and sustain funding over an extended period.
Strategic Implementation
Yves emphasized the dual approach of providing immediate liquidity for critical operations like middleware and RAM management while implementing a vesting schedule for other buckets to prevent market flooding and ensure gradual integration of tokens into the market. This strategy is designed to balance the immediate functional needs of the EOS Network with long-term economic and operational stability, aligning with typical market dynamics where gradual token release mitigates volatility and ensures a predictable market supply.
The structured and phased approach to token distribution reflects a significant shift in EOS’s economic model, aimed at enhancing both the appeal and the financial stability of the EOS ecosystem in a rapidly evolving blockchain environment.
A Focus on Market Making
The technical discussion on RAM management within the EOS ecosystem primarily centered on the strategic initiatives to manage and enhance the market for RAM through market making. Yves La Rose outlined the ENF’s plans for engaging actively in market making for RAM on the EOS Network, aiming to stabilize and potentially increase demand and utilization of RAM, which is crucial for the network’s economic model and operational efficiency.
Yves explained that effective market making in RAM requires not only strategic planning in terms of when and how tokens are released to market makers but also a careful selection of market makers who can responsibly manage the supply and demand dynamics of the market.
By providing liquidity and more consistent pricing, the ENF aims to foster a more reliable and dynamic environment for all stakeholders in the EOS ecosystem.
Stakeholder Engagement and Incentive Alignment
Yves emphasized the crucial role of stakeholder feedback in shaping the EOS tokenomics, highlighting the importance of active community involvement for the success of strategic changes. He detailed how the ENF uses community forums, direct consultations, and insights from Block Producer calls to effectively refine proposals and address community concerns.
Yves emphasized the ENF’s role in being responsive to the community’s needs by acting as a mirror that reflects feedback from token holders. In crafting recommendations, the ENF adopts a strategic approach, aiming for what Yves describes as the “highest, lowest common denominator.” This method involves creating proposals broad enough to avoid the pitfalls of being overly niche or detailed, which historically has made achieving consensus on EOS challenging. By carefully balancing this concept, the ENF ensures the proposals are inclusive and broad-reaching, securing wide support while still reflecting the collective priorities and detailed feedback from the community. This balanced approach allows the EOS ecosystem to evolve in alignment with the needs and inputs of its stakeholders, with the Block Producers ultimately deciding which initiatives to pursue.
Alignment of Incentives
The strategic redesign of EOS tokenomics aims to align the incentives of key stakeholders—ENF, Labs, and EOS Block Producers—with the ecosystem’s long-term health and market performance. This realignment ensures that:
- EOS Network Foundation (ENF): Receives sustained funding and operational capacity to lead core development, strategic coordination, and ecosystem communications, ensuring long-term growth and stability of the EOS Network.
- EOS Labs: Is empowered to focus on the incubation and acceleration of emerging projects, significantly contributing to the ecosystem’s long-term health and market performance. This role streamlines the development and funding of new initiatives, enhancing the overall competitiveness of the EOS ecosystem.
- Block Producers: Are incentivized to maintain network security, integrity, and uptime, ensuring continuous updates and investments in EOS infrastructure. This commitment enhances the overall stability and advancement of the EOS ecosystem.
- Token Holders: Gain new incentives for locking up their tokens, including enhanced staking rewards. Their participation supports the RAM market by locking up more EOS in the Bancor pool and rewards those holding RAM, further stabilizing and enriching the EOS ecosystem.
Yves highlighted how the revised tokenomics connect the success of individual stakeholders to the broader market performance of EOS tokens, fostering a cycle of growth and investment that benefits the entire ecosystem.
Conclusion on Stakeholder Engagement
Concluding, Yves emphasized the mutual benefits of these redesigned incentive structures, which create a conducive environment where the success of EOS directly boosts its stakeholders, promoting a committed and engaged community. He underscored the ENF’s commitment to ongoing dialogue and adaptability, noting that the tokenomics and incentive structures are designed to evolve with the ecosystem’s needs and the emergence of new challenges and opportunities. This approach ensures that EOS remains competitive and responsive to the dynamic demands of the blockchain market.
Q & A
Q: What is the strategic rationale behind the specific token allocations, especially considering the substantial reduction in the total supply?
A: The token allocations were strategically designed to broaden EOS’s appeal within the cryptocurrency market and to facilitate easier consensus among stakeholders, which is crucial for the adoption of the new tokenomics. These allocations were based on extensive feedback and modeling to ensure they meet the needs of various participants in the EOS ecosystem, such as developers, investors, and block producers. This strategic approach helps maintain EOS’s competitive edge and ensures its sustainability as a leading blockchain platform.
Q: What entity will be signing the contracts with market makers?
A: The EOS Network Foundation (ENF) will handle contracts with market makers. Currently, no agreements are in place because we need to secure the necessary tokens first. Once we have the tokens, we plan to collaborate with various market makers, including selling tokens directly or loaning them for market-making purposes.
The main use of these tokens will be to purchase RAM, which is crucial for effective market making. Market makers will receive tokens in tranches based on their liquidity analysis, allowing for strategic, adaptive market involvement. This setup will enable us to start providing liquidity on both centralized and decentralized exchanges for the first time, using multiple market makers to enhance market stability.
Q: Would you be willing to, in your quarterly report, talk about where the RAM market making funds are going, including which market makers are involved or how much you allocated in that particular quarter?
A: Yes, we can provide details similar to what we’ve shared previously. We will engage third-party firms to audit liquidity on exchanges. These audits help us ensure transparency about how the funds are used and verify the activities of market makers involved in RAM trading.
We can make these audit reports public, giving stakeholders a clear view of the market activities and any discrepancies highlighted by the third party. This approach enables us to maintain oversight and address any issues with market makers according to our agreements.
While we can’t disclose specific transaction timings to prevent front-running, we are committed to sharing the general outcomes and strategic insights post-facto, ensuring stakeholders have visibility into how funds are being allocated and used.
Closing Session Summary
Yves outlined that the new tokenomics proposal is open for Block Producer review. He explained that if there is general support, the ENF will move forward with preparing the proposal for a community vote, allowing stakeholders ample time for consideration. He stressed that the ultimate decision lies with the Block Producers, reminding them of their freedom to vote as they see fit once the proposal reaches the decision stage on-chain.
Expressing his gratitude for the community’s active participation, Yves conveyed optimism about EOS’s future, driven by robust discussions and proactive community initiatives. He reiterated that the direction of further developments, whether to continue, adjust, or cease efforts on tokenomics, would depend entirely on the guidance from the Block Producers.
Concluding the meeting, Yves thanked everyone for their collaborative efforts and looked forward to the decisions that will shape EOS’s strategic direction and operations. With a final note of appreciation, he officially adjourned the meeting.
Resources
EOS Tokenomics Data Spreadsheet
Block Producer Attendee List
- Big.ONE
- Crypto Lions
- Defibox
- Detroit Ledger Technology
- EOSeoul
- EOS Asia
- EOSIO.SG
- EOSLaoMao
- EOS Nation
- EOS Pizza
- EOS RIO
- EOSphere
- EOSSupport
- EOS Titan
- EOSUSA
- GenerEOS
- Greymass
- Newdex
- SlowMist
- StartEOS
EOS Network
The EOS Network is a 3rd generation blockchain platform powered by the EOS VM, a low-latency, highly performant, and extensible WebAssembly engine for deterministic execution of near feeless transactions; purpose-built for enabling optimal Web3 user and developer experiences.
EOS Network Foundation
The EOS Network Foundation (ENF) was forged through a vision for a prosperous and decentralized future. Through our key stakeholder engagement, community programs, ecosystem funding, and support of an open technology ecosystem, the ENF is transforming Web3. Founded in 2021, the ENF is the hub for EOS Network, a leading open source platform with a suite of stable frameworks, tools, and libraries for blockchain deployments. Together, we are bringing innovations that our community builds and are committed to a stronger future for all.


